Al-Biruni: The Polymath Who Measured the Earth

Al-Biruni (973–1048 CE) was a pioneering Muslim scholar whose contributions spanned astronomy, mathematics, geography, and anthropology. Born in Kath (modern Uzbekistan), his insatiable curiosity led to groundbreaking discoveries, including precise Earth measurements and cross-cultural studies. His works, such as Tahqiq ma li’l-Hind, influenced both Islamic and European scholars. A true polymath, Al-Biruni’s scientific rigor and interdisciplinary approach shaped modern knowledge, leaving a lasting intellectual legacy that continues to inspire researchers today.
Early Life and Education
Al-Biruni was born in 973 CE in Kath, a city in present-day Uzbekistan. From a young age, he displayed a deep curiosity for science and philosophy. He studied under renowned scholars and gained knowledge in mathematics, astronomy, and natural sciences. Despite political instability, he continued his intellectual pursuits, traveling across regions to exchange ideas. Influenced by Greek, Indian, and Persian traditions, his rigorous studies laid the foundation for his groundbreaking contributions to multiple scientific fields.
Major Contributions
A. Astronomy and Mathematics
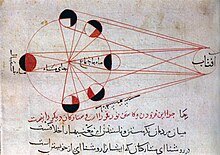
Al-Biruni made significant advancements in astronomy and mathematics. He conducted precise astronomical observations, improving calculations of planetary motion. He estimated the Earth’s circumference with remarkable accuracy, coming close to modern values. His studies on Earth’s rotation and the relationship between time and celestial movements contributed to the foundation of modern astronomy.
B. Geography and Cartography
His work in geography and cartography was groundbreaking. In Kitab al-Tafhim, he explained astronomical and geographical principles. He developed methods for measuring distances and geographical coordinates with precision. His insights into map-making and the concept of time zones influenced later geographical studies.
C. Physics and Natural Sciences
Al-Biruni’s contributions to physics included studies on motion, gravity, and density. His experiments in hydrostatics helped in understanding fluid mechanics. He also conducted research in mineralogy, categorizing various substances based on their physical properties.
Legacy and Influence
Al-Biruni’s works were widely translated into various languages, influencing both Islamic and European scholars. His contributions to astronomy and mathematics shaped the research of figures like Copernicus and Kepler. As a pioneer of Indology, his comparative studies of cultures and religions laid the foundation for modern anthropology. His interdisciplinary approach continues to serve as a model for scientific inquiry, cementing his status as one of history’s greatest polymaths.
Conclusion
Al-Biruni’s groundbreaking contributions to astronomy, mathematics, and cultural studies establish him as one of the greatest scholars of the Islamic Golden Age. His scientific rigor, interdisciplinary research, and comparative approach to knowledge influenced both the Islamic and Western worlds. His legacy continues to inspire modern scientists and historians alike. Exploring his works offers valuable insight into the rich intellectual heritage of Muslim scholars and their lasting impact on global knowledge.


